Understanding the Circular Economy
The circular economy is an economic model that aims to eliminate waste and promote the continuous use of resources, ultimately leading to a more sustainable and efficient system. In contrast to the traditional linear economy, which follows the 'take, make, dispose' approach, the circular economy is centered on three key principles: reduce, reuse, and recycle. In this section, we will explore the concept of the circular economy and its benefits.
The illustration below shows a slightly simplified and idealized version of the circular economy. In reality, the circular economy is much more complex, but this illustration should give you a good idea of what it is all about.
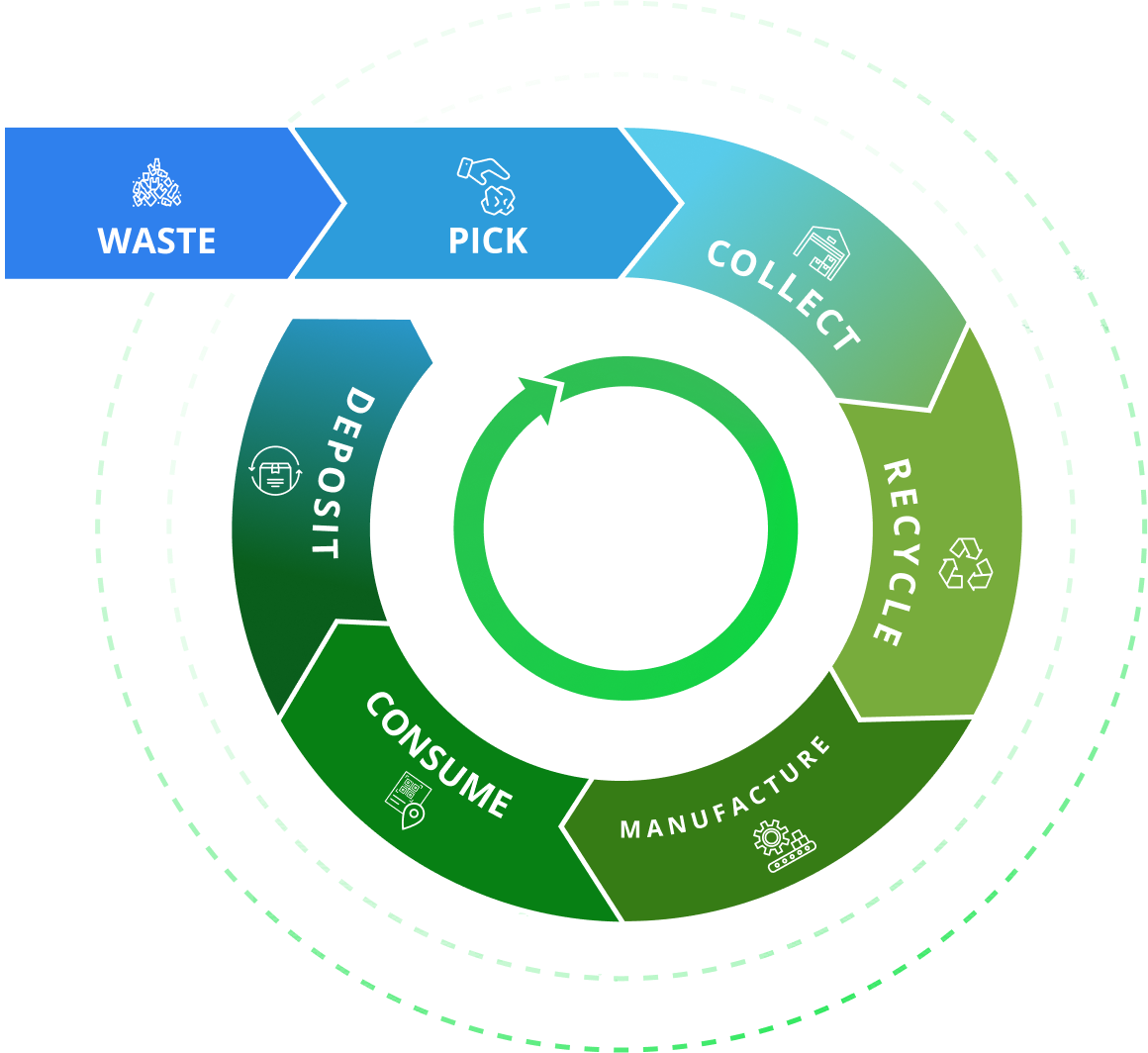
Why is the Circular Economy important?
Plastic waste can currently be found in your blood. It is in the air you breathe and the water you drink. It is in the food you eat and the clothes you wear. It is everywhere. We don't know the long-term effects of plastic waste on our health, but we can assume that having toxic chemicals in our bodies is not a good thing.
We are ruining the environment and ourselves in countless ways (plastic waste is just one of them), and wasting resources on top of it all. Circular economy is a way to address these issues and create a more sustainable future for all of us. It is aimed at eliminating waste and promoting the continuous use of resources, ultimately leading to a more efficient system.
When we make circular economy work, we can:
- Save ourselves
- Save (and make) money
Principles of the Circular Economy
The circular economy is centered on three key principles: reduce, reuse, and recycle. Let's take a closer look at each of these principles.
Reduce
The first principle of the circular economy is to minimize the consumption of finite resources and reduce waste generation. This involves designing products and services that use fewer resources, adopting efficient production methods, and promoting sustainable consumption practices.
Reuse
The circular economy encourages the reuse of products and materials for as long as possible to maximize their value. This can be achieved through practices such as refurbishment, remanufacturing, and sharing or leasing products instead of purchasing them outright.
Recycle
When products or materials can no longer be reused, recycling comes into play. In a circular economy, waste is viewed as a valuable resource that can be transformed into new materials or products. This approach not only helps reduce waste but also conserves natural resources by decreasing the demand for virgin materials.
First things first
To put these principles into a more concrete form, let's use plastics as an example. The world is full of plastic waste and only keeps putting more pollution into the environment. For a practical solution to work, we need to not only address new production but also the existing waste. With this reality in mind we can prioritize like this:
- Close the tap: Stop more waste from entering the environment. If you had a leak in your house, you would first close the tap before cleaning up the mess.
- Clean it up: Clean up the existing waste. This is a huge task, but it is necessary to prevent further damage to the environment.
- Provide recycling aid: Physical and digital infrastructure is lacking in many places. We need to provide the tools and infrastructure needed for recycling to work everywhere.
What is needed for the Circular Economy to work?
The circular economy is not a single thing, nor a single silver bullet solution. Instead, it requires many forces to work together. Working together being the key here.
To implement circular economy, some of the things we need to do are:
- Create and invest in digital and physical infrastructure available to everyone
- Adapt financial models and consumer behavior to align with circular economy principles.
- Create incentives for people to use the infrastructure
- Create incentives for organizations to collaborate
- Redesign products and services to be more circular
- Develop supportive policies and regulations that incentivize and enable circular practices.
- Establish standardized metrics and reporting systems to track progress and share best practices.
- Raise awareness
This is somewhat simplified, but it gives a good idea of what is needed for the circular economy to work. EmpowerChain aims to tackle the digital infrastructure and incentives part of the equation.